We have always been learning about how photosynthesis takes place and how important it is in order to keep the world going and useful to evolve oxygen and produce food, but without chloroplast photosynthesis wouldn’t have been possible. In this article we are going to be reading about chloroplast.
Table of Contents
What is chloroplast ?
Chloroplast is a lens-shaped, polymorphic (occurs in many forms), green coloured plastid and a living cell organelle. These are present in mesophyll cells of the leaves in all green plants. They are self regulating and self replicating because of the presence of nuclei acid.
Chloroplast consists of proteins, lipids, photosynthetic pigments, ribosomes, RNA, plasidome (DNA of chloroplast), vitamins and certain traces of metal ions. Here, physical energy from the sun is converted into chemical energy and the process of photosynthesis begins.
Structure of chloroplast:
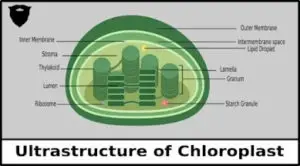
The chloroplast is a double membrane structure. The outer membrane is made up of lipoproteins and is selectively permeable. Each membrane is 40 to 60 Å thick and space between both the membranes is 25 to 75 Å. Both the membranes collectively are called peristromium.
The space between the two membranes is called periplastidial space or outer chamber and the inner membranes encloses the inner chamber which consists of stroma (colourless, colloidal matrix). The stroma contains enzymes which are required for photosynthesis, starch grains and osmophilic droplets of vitamin K. Dark reaction takes place in stroma.
Stroma consists of 40 to 60, green coloured grana (Sigular – Granum). Granum is made up of thylakoids which are small and disc like containing photosynthetic pigment. Thylakoids form a stack of grana. The thylakoid is covered with thylakoid membrane or grana lamellae where light reaction takes place.
Grana lamellae (made up of phospholipids and proteins) contains ultramicroscopic units called quantasomes which give granular appearance to the thylakoid. Quantasomes are flattened, sphere shaped, containing pigments like chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b, carotenes and xanthophylls which forms a pigment system. Each quantasome has 230 chlorophyll molecules.
One stack of grana is interconnected to another stack by membranes called stroma-lamellae or intergrana or fret channels. This helps in transporting the materials faster. ATP synthesis takes place in grana.
Composition of chloroplast:
| Content | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Protein | 40-50% |
| Chlorophyll | 7-10% |
| RNA | 2-5% |
| DNA | 1% or less |
| Phospholipids | 23-25% |
| Carotenoids | 1-2% |
| Enzymes and co-enzymes | Small amount |
| Fe, Cu, Zn, Mn and Mg | Small amount |
Different types of chloroplast:
Following are the different types of chloroplast:
**image**
Functions of chloroplast:
Following are the functions of chloroplast:
- In eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast in the presence of sunlight.
- These are the natural machines for the synthesis of energy rich organic compounds like sugar, starch, etc..
- It maintains the balance of CO2 and O2 in the environment by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and releasing O2 which is essential for cellular respiration for living beings.
FAQ:
1. What is the function of chloroplast ?
Ans:In eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast in the presence of sunlight. These are the natural machines for the synthesis of energy rich organic compounds like sugar, starch, etc.. It maintains the balance of CO2 and O2 in the environment by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and releasing O2 which is essential for cellular respiration for living beings.
2. What is the structure of chloroplast ?
Ans: Chloroplast is a double membranous structure found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves.
3. What are the types of chloroplast ?
Ans: Different types of chloroplast are stellate shaped, cup shaped, discoid shaped, C-shaped, reticulate, spiral, gridle shaped and ribbed shaped.
4. Why are chloroplast green ?
Ans: Chloroplast are green in colour because they show presence of chlorophyll which gives it a green colour.
5. Can chloroplast grow back ?
Ans: Yes, they are self-replicating and self-regulating because of the presence of nuclei acid.
6. Where is chloroplast present ?
Ans: Chloroplast is present in the mesophyll cells of the leaves.
7. Why are chloroplast found in plant cells only ?
Ans: Since, it is essential for photosynthesis it is present only in the plant cells and not animal cells.